Welcome to our comprehensive guide on peptic ulcers. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, treatment options, and prevention tips for peptic ulcers. If you or someone you know is suffering from this condition, it's important to understand its underlying factors and how to manage it effectively. So, let's dive in!
Outline
- Peptic Ulcer
- Causes of Peptic Ulcers
- Common Symptoms
- Diagnosing Peptic Ulcers
- Treatment Options
- Medications for Peptic Ulcers
- Lifestyle Changes for Managing Peptic Ulcers
- Complications of Peptic Ulcers
- Prevention Tips
- Diet Recommendations for Peptic Ulcer Patients
- Home Remedies for Peptic Ulcers
- When to Seek Medical Attention
- Conclusion
- FAQs
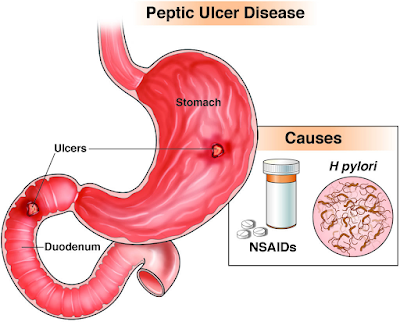
Peptic Ulcer
A peptic ulcer refers to an open sore that forms in the lining of the stomach, upper small intestine, or esophagus. It occurs when the protective mucus layer in these areas gets damaged, allowing stomach acids to erode the underlying tissues. Peptic ulcers can be categorized into two types: gastric ulcers, which develop in the stomach lining, and duodenal ulcers, which occur in the upper part of the small intestine.
Causes of Peptic Ulcers
The primary cause of peptic ulcers is a bacterial infection known as Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori). This bacterium weakens the protective mucous layer, making the stomach and intestine more susceptible to damage from digestive acids. Other factors that can contribute to the development of peptic ulcers include long-term use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as aspirin or ibuprofen, excessive alcohol consumption, smoking, and high levels of stress.
Common Symptoms
Peptic ulcers often present with a variety of symptoms, which may vary from person to person. Some common signs to watch out for include:
- Burning or gnawing abdominal pain, usually occurring between meals or during the night
- Nausea and vomiting
- Indigestion or heartburn
- Unexplained weight loss
- Loss of appetite
- Dark or black stools (indicating the presence of blood)
- Fatigue or weakness
Diagnosing Peptic Ulcers
If you experience persistent symptoms suggestive of peptic ulcers, it's crucial to consult a healthcare professional. They will perform a thorough evaluation, which may involve:
- Reviewing your medical history and symptoms
- Conducting a physical examination
- Recommending diagnostic tests like endoscopy, upper gastrointestinal series, or H. pylori testing
- Taking a tissue sample (biopsy) during an endoscopy to rule out other conditions like stomach cancer
Treatment Options
The treatment of peptic ulcers typically involves a combination of medications, lifestyle changes, and, in some cases, surgery. The primary goals of treatment are to relieve symptoms, promote healing, prevent complications, and eradicate the H. pylori infection if present. It's important to follow your healthcare provider's recommendations for the best outcomes.
Medications for Peptic Ulcers
Several types of medications may be prescribed to manage peptic ulcers:
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs): These drugs reduce stomach acid production, allowing the ulcer to heal. Examples include omeprazole, lansoprazole, and esomeprazole.
Histamine H2-receptor antagonists: These medications also reduce acid production and promote healing. Famotidine and ranitidine are commonly used H2 blockers.
Antacids: These provide temporary relief by neutralizing stomach acid. They are often used in combination with other medications.
Antibiotics: If H. pylori infection is detected, a course of antibiotics will be prescribed to eradicate the bacteria.
Lifestyle Changes for Managing Peptic Ulcers
In addition to medications, making certain lifestyle modifications can aid in managing peptic ulcers. Consider the following recommendations:
- Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, as they can worsen symptoms and delay healing.
- Practice stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
- Eat smaller, more frequent meals to reduce stomach acid production and prevent irritation.
- Limit or avoid foods and beverages that trigger symptoms, such as spicy foods, caffeine, and acidic fruits.
- Maintain a healthy weight and exercise regularly to improve overall digestive health.
Complications of Peptic Ulcers
If left untreated, peptic ulcers can lead to severe complications, including:
Bleeding ulcers: When an ulcer erodes blood vessels, it can cause internal bleeding, leading to anemia or even life-threatening situations.
Perforation: In rare cases, ulcers can create a hole through the stomach or intestine wall, causing infection and inflammation in the abdominal cavity.
Gastric outlet obstruction: Scarring from ulcers can narrow the digestive tract, blocking the passage of food and causing vomiting and weight loss.
Prevention Tips
Preventing peptic ulcers involves addressing the underlying causes and adopting healthy habits. Here are some essential tips:
- Wash your hands regularly to reduce the risk of H. pylori infection.
- Avoid long-term use of NSAIDs, or use them under medical supervision.
- Consume a well-balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Manage stress levels through relaxation techniques and activities you enjoy.
- Limit alcohol consumption and quit smoking.
Diet Recommendations for Peptic Ulcer Patients
While there isn't a specific "ulcer diet," certain dietary guidelines can help manage symptoms and promote healing. Consider the following:
- Consume fiber-rich foods like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
- Include probiotic-rich foods like yogurt, sauerkraut, and kefir to support gut health.
- Opt for lean proteins such as fish, poultry, beans, and tofu.
- Avoid spicy foods, greasy/fried foods, and foods that cause discomfort or trigger symptoms.
- Stay adequately hydrated by drinking enough water throughout the day.
Home Remedies for Peptic Ulcers
Alongside medical treatment, some home remedies may provide relief from peptic ulcer symptoms:
Aloe vera juice: Known for its soothing properties, aloe vera juice can help reduce inflammation and promote healing.
Cabbage juice: Drinking cabbage juice has been suggested to aid in ulcer healing due to its high glutamine content.
Licorice root: Deglycyrrhizinated licorice (DGL) supplements may help protect the stomach lining and alleviate symptoms.
Honey: Its antimicrobial properties can potentially help fight H. pylori infection, but further research is needed.
Remember, home remedies should complement professional medical advice and not replace it.
When to Seek Medical Attention
It's important to seek immediate medical attention if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- Severe or persistent abdominal pain
- Vomiting blood or dark, tarry stools
- Difficulty swallowing or unexplained weight loss
- Sudden, sharp abdominal pain radiating to the back
- Fainting, dizziness, or signs of anemia
Conclusion
Peptic ulcers can cause significant discomfort and potentially lead to complications if not properly managed. By understanding the causes, symptoms, treatment options, and prevention tips discussed in this article, you are better equipped to navigate this condition. Remember to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
FAQs
1, Can stress cause peptic ulcers?
While stress does not directly cause peptic ulcers, it can worsen symptoms and delay healing. Stress management techniques can be beneficial for overall well-being.
2. Can I take over-the-counter pain relievers for peptic ulcers?
It's best to consult your healthcare provider before taking any medications, including over-the-counter pain relievers, as they can aggravate peptic ulcer symptoms.
3. Is surgery always required for peptic ulcers?
Surgery is typically reserved for cases where complications arise or if other treatments have been ineffective. Most peptic ulcers can be managed with medication and lifestyle changes.
4. Can peptic ulcers be cured completely?
With appropriate treatment, most peptic ulcers can heal completely. However, it's crucial to follow the recommended treatment plan and make necessary lifestyle adjustments to prevent recurrence.
5. Are peptic ulcers contagious?
No, peptic ulcers are not contagious. They are primarily caused by the H. pylori bacterium or other factors like NSAID use and lifestyle habits.

0 Comments
if you have more queries about this page please let me know